Feel the moment!
Who doesn’t enjoy a refreshing escape from the heat during a nice swim, a relaxing boat ride, a run, or a nice workout outside – or simply just a day at the beach?
Spending time outside is highly rejuvenating, but it’s important to protect your skin from the sun – and especially the reflecting elements, that increases your exposure. Between prolonged sun exposure, sweating and spending time in the water or in the snow, there are plenty of opportunities to get sunburned. And just like a proper preparation for a football match, like shoes, shin guards and a team strategy, it is key to remember applying and re-applying sun protection.
There are many factors that can contribute to a painful sunburn during outdoor activities. Altitude, sea levels, reflections from surfaces are just some of the elements, that can damage your skin. That is why we’ve created this guide to sun protection for outdoor activities, so that you can enjoy the activities that you love, without worrying about sunburns and skin damage.

Water sports:
There is nothing that can recreate your inner child like a playful day in the water. Whether you get high on adrenalin on the surfboard, love a nice, active swim or just a day on the beach or by the pool, you need to be especially careful when it comes to protecting yourself from the sun. Not only does the water increase the amount of UV, as it reflects the sun’s rays – the cooling effect of the water makes you think that you are not getting burned. Talk about a highly dangerous cocktail! As always sun protection is your best companion and you should apply high factor, broad-spectrum, water-resistant sun protection at least 20 minutes before you head out to enjoy the day by the water. And don’t forget to re-apply as the hours go by.
Did you know that P20 Original is highly water resistant?
Winter sports:
Higher altitudes increase your risk of sun damage, as the UV exposure increases by roughly 5% with every 1.000 feet (300 meter) above the sea level. Meaning that an altitude of 10.000 feet (3km) above sea level can give you radiation that can be as much as 45% stronger. And in addition, the snow acts as a reflective surface, bouncing the suns UV rays back towards you for a double dose of exposure.
A high factor, broad spectrum sunscreen is the only way forward. Be sure to cover all areas – even the nostrils, as they are extra exposed to the sun, when the UV rays reflects upwards off the snow’s surface.
Did you now that all P20 products contain broad spectrum UVA- and UVB-protection?
Extreme sports:
Compared to dangling from a cliff on a rock climb or going fast downhill on a mountain bike, you might think the risk of sun damage is trivial. Sun damage can be just as fatal when you are sweating in the sun without protection. Here is why. If you enjoy activities that requires extreme effort, you most likely will spend prolonged amounts of time in the sun, as well as at high level of altitudes or in the water. Wearing a broad-spectrum sunscreen that is specially formulated to outdoor activities and maintains a high SPF, will help you limit your exposure to UVA and UVB rays.
Did you know that all P20 sun products protects up to hours?
Competitive sports:
Football, tennis, a marathon – you name it – a sport played outside, requires a large amount of time both training and competing. And as essential it is to stay in shape and do it your best, as crucial it is to protect yourself from the sun. Even on a cloudy day, where up to 80% of UV rays are still beaming down on your skin. It takes measures to perform at your best – and sun protection is one of them. Using a specially formulated sunscreen that retains its protection when your skin is sweating heavily, will protect your skin while you are training and competing.
Did you know that P20 Original Lotion, Spray and Continuous Spray are sweat resistant?
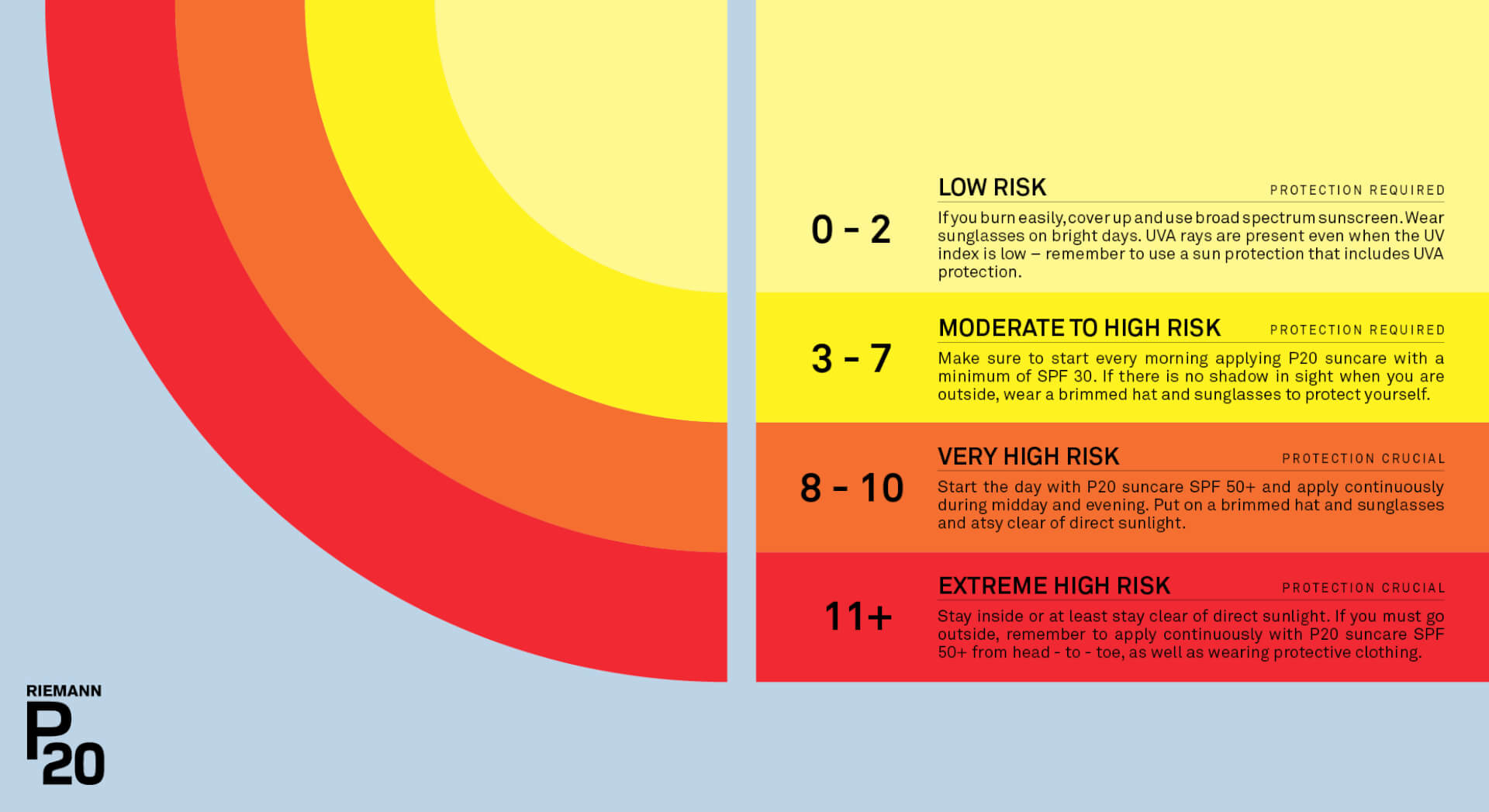
So, how can you keep track of the daily UVA and UVB level? Enter The UV Index – a tool, developed by WHO, to determine how much UV radiation you are surrounded by. To identify the daily index, there are a variety of weather apps, that can guide you to the best precaution against UV radiation. Let’s break down the index:
- Index 0-2: Low risk and protection is required- If you burn easily, cover up and use broad spectrum sunscreen. Wear sunglasses on bright days. UVA rays are present even when the UV index is low – remember to use a sun protection that includes UVA protection.
- Index 3-5: Moderate risk and protection is required – Generously apply broad-spectrum sunscreen, even on cloudy days, and after swimming or sweating. Stay in the shade during midday when the sun is strongest. When outdoor use a wide-brimmed hat, and UV-blocking sunglasses.
- Index 6-7: High risk and protection is required – Generously apply broad-spectrum sunscreen, even on cloudy days and after swimming or sweating. Stay out of the sun between 11am and 3pm. When outdoor, seek shade, wear protective clothing, a wide-brimmed hat, and UV-blocking sunglasses.
- Index 8-10: Very high risk and protection is crucial – Generously apply broad-spectrum sunscreen, even on cloudy days and after swimming or sweating. Stay out of the sun between 11am and 3pm. When outdoor, seek shade, wear protective clothing, a wide-brimmed hat, and UV-blocking sunglasses.
- Index 11+: Extreme high risk and protection is crucial – Generously apply broad-spectrum sunscreen, even on cloudy days and after swimming or sweating. Stay out of the sun between 11am and 3pm. When outdoor, seek shade, wear protective clothing, a wide-brimmed hat, and UV-blocking sunglasses.
The UV Index changes throughout the day and is usually strongest during midday. But it’s important to notice, that UV rays are always present, and we highly recommend that you use P20 sun protection every day, all year.

